Today is Veterans Day in the United States.
Today is Remembrance Day in Canada, and similar holidays in many other countries.
Today is also Polish Independence Day, commemorating the restoration of Polish independence on this day in 1918.
Today is also the Memorial of St. Martin of Tours, 316-397, the Patron Saint of Horsemen.
St. Martin, it should be noted, had been a Roman officer, albeit a reluctant one, who took up that position due to the insistence of his family. He's famously depicted on horseback, giving his cloak to a naked figure he encountered en route. He left the Roman military to become a priest, and ultimately became a Bishop.
St. Martin's feast day used to be celebrated in Poland in a manner which included baking horseshoe cookies "for his horse". The recipe:
INGREDIENTS
1 cup butter or margarine
1/2 cup confectioners' (powdered) sugar
2 teaspoons vanilla
2 cups sifted all-purpose flour
1/2 teaspoon salt
1 cup quick-cooking rolled oats, uncooked
Makes three dozen cookies.
Cream butter or margarine; add sugar gradually while continuing to cream; beat until fluffy. Stir in vanilla, flour, and salt. Blend in rolled oats. Roll out about 1/4 inch thick on lightly floured board. Cut in strips 6 inches long and 1/2 inch wide. On ungreased cookie sheets shape strips to resemble horseshoes. Bake at 325° for 20 to 15 minutes or until lightly browned.
1620 Pilgrims execute the Mayflower Compact, one of the founding charters of American democracy.
The original document has not survived, but several early copies have. There are slight differences in spelling and punctuation, but basically the text reads as follows:
In the name of God, Amen. We, whose names are underwritten, the loyal
subjects of our dread Sovereign Lord King James, by the Grace of God, of
Great Britain, France, and Ireland, King, defender of the Faith, etc.
Having undertaken, for the Glory of God, and advancements of the
Christian faith and honor of our King and Country, a voyage to plant the
first colony in the Northern parts of Virginia, do by these presents,
solemnly and mutually, in the presence of God, and one another, covenant
and combine ourselves together into a civil body politic; for our
better ordering, and preservation and furtherance of the ends aforesaid;
and by virtue hereof to enact, constitute, and frame, such just and
equal laws, ordinances, acts, constitutions, and offices, from time to
time, as shall be thought most meet and convenient for the general good
of the colony; unto which we promise all due submission and obedience.
In witness whereof we have hereunto subscribed our names at Cape Cod the
11th of November, in the year of the reign of our Sovereign Lord King
James, of England, France, and Ireland, the eighteenth, and of Scotland
the fifty-fourth, 1620.[
1817 Francisco Xavier Mina and 25 compatriots executed at Fort San
Gregorio for insurrection.
1864 The Lincoln Mining District, the first mining district near South Pass, organized. Attribution: Wyoming State Historical Society.
1865 The U.S. Army renamed Fort Connor to
Fort Reno in honor of Major General Jesse L. Reno.
1886 George W. Baxter assumes the office of Territorial Governor. He resigned on December 20 of the same year. Given his very brief stint as Territorial Governor, questions would have to be raised as to whether or not he wanted the job, or simply agreed to take it at the request of President Cleveland, who was then in office and who had removed F. E. Warren.
On the same day, Francis E. Warren stepped down as Territorial Governor at the request of President Cleveland. Questions regarding dealings with a Cheyenne Wyoming businessman caused his resignation, but his reputation would prove intact, and he would resume the position in 1889, and keep it until 1890 when became Wyoming's first elected State Governor. He went on to become a US Senator from November 1890 until 1893, and then again until his death on November 24, 1929. He was John J. Pershing's father in law.
1890 The Wyoming Supreme Court meets for the first time.
1918 On this day, Ninety years ago, World War One ended. The Armistice became effective at 11:00. Since hostilities had commenced in 1914, 9,000,000 soldiers had died in action, 21,000,000 had been wounded, and many additional soldiers civilians had died due to the direct and indirect consequences of the war, not the least of which was the unleashing of the Spanish Flu in military camp conditions, which would claim more lives than combat had. The German, Russian and Austro-Hungarian Empires had been destroyed with no real ability for a successful popular democratic ideal to take root in those nations, which fell into turmoil. Communism and similar movements, previously occupying the fringe of the Socialist left, filled in the vacuum resulting in violent revolution in various localities including Russia and Germany, achieving power in Russia and failing to do so in Germany, which was none the less left in turmoil. New nations, such as Poland, Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia were born, or resumed their positions on the map after having not had them for centuries. The German Imperial Army, refusing to go down with the Kaiser, had effectively arranged for his surrender of power and fully assumed the status of a power unto itself, with grave consequences for the future. Japan, ascendant since the late 19th Century, had seized territory in the East as an Allied power. Ireland had gone into revolution over the issue of conscription, and the UK was left with a guerrilla war in Ireland. The Ottoman Empire had collapsed and Turkey was born, with the war against Turkey still going on. The former Ottoman possession in the Middle East were now European territories. The United States, which had sat on the fence of world power status for decades, briefly assumed that role, and then retreated from it. The Dominions of Canada and Australia had entered the war as confirmed dominions and left it much more independent nations. In spite of the inconclusive results, to some extent, and the views later held in later eras, the war was regarded as worthwhile and a victory in the English speaking world at this time.
In Wyoming, World War One had caused a very significant economic boom which very much predated the US entry into the war. Starting in 1914, British Remount agents scoured the United States for suitable military horses, purchasing thousands, and causing a horse boom in Wyoming which lasted throughout the war, as the US later began to do the same. Cattle prices also rose as the demand for meat rose due to the war. Homesteading received its last great boom, which would peak in 1919, the last year that the American farmer achieved economic parity with the urban middle class.
Oil exploration massively accelerated during the wear, causing towns like Casper to boom, and which resulted in Casper's first "sky scraper", the Oil Exchange Building, now the Consolidated Royalty Building.
The day became a holiday in many countries following World War One, and is recalled today under a variety of names. It is a Federal holiday in the Unites States, being known as Veterans' Day, having come to honor American veterans of all wars.
Some poetry from the last war to inspire a fair amount of important poetry, but which speaks to all wars.
In Memoriam
by Ewart Alan Mackintosh (who himself was killed in action).
(Private D Sutherland killed in action in the German trenches, 16 May 1916, and the others who died.)
So you were David's father,
And he was your only son,
And the new-cut peats are rotting
And the work is left undone,
Because of an old man weeping,
Just an old man in pain,
For David, his son David,
That will not come again.
Oh, the letters he wrote you,
And I can see them still,
Not a word of the fighting,
But just the sheep on the hill
And how you should get the crops in
Ere the year get stormier,
And the Bosches have got his body,
And I was his officer.
You were only David's father,
But I had fifty sons
When we went up in the evening
Under the arch of the guns,
And we came back at twilight -
O God! I heard them call
To me for help and pity
That could not help at all.
Oh, never will I forget you,
My men that trusted me,
More my sons than your fathers',
For they could only see
The little helpless babies
And the young men in their pride.
They could not see you dying,
And hold you while you died.
Happy and young and gallant,
They saw their first-born go,
But not the strong limbs broken
And the beautiful men brought low,
The piteous writhing bodies,
They screamed 'Don't leave me, sir',
For they were only your fathers
But I was your officer.
And my favorite, In Flanders Fields, by Canadian John McCrae, who died of the Influenza Epidemic during the war, while serving in France.
In Flanders fields the poppies blow
Between the crosses, row on row,
That mark our place; and in the sky
The larks, still bravely singing, fly
Scarce heard amid the guns below.
We are the Dead. Short days ago
We lived, felt dawn, saw sunset glow,
Loved and were loved, and now we lie,
In Flanders fields.
Take up our quarrel with the foe:
To you from failing hands we throw
The torch; be yours to hold it high.
If ye break faith with us who die
We shall not sleep, though poppies grow
In Flanders fields.
"To Our Hero's". Cemetery Wall in Paris, France. France's contribution to the Allied victory in World War One surpasses that of any other Allied nation. . .something you'd sometimes not realize if you only read the English language accounts of the war. MKTH photograph.
On this date in 1918, the Great War came to an end.*

Usually such posts are highly retrospective, and I suppose this one will be to a degree, but not in the "oh what a terrible waste" fashion that so many of them are. The "Oh, What A Lovely War" view of the war popularized by the posthumous post World War Two publication of Siegfried Sassoon's poetry is largely baloney.** In reality, the view taken earlier, that Germany was a horrible world menace on the European stage ruled by its military and a few autocrats who cared little about the rivers of blood they were spilling in order to impose Germany's imperial will on Europe is much closer to reality.

Indeed, its telling that in order to being the peace about, it had to occur in the context of a German revolution. That revolution threatened for a time to make former Imperial Germany into a communist Soviet state, and put the new provisional government in the position of having to put down a left wing revolution. That alignment, and the unrepentant view of Germany's hard right and its military would guaranty a second war, not the supposedly "harsh" terms of the Versailles Treaty. A hard won victory, therefore, would not bring lasting peace, but that too really isn't for the reasons so often cited.

Indeed, had the provisions of the Versailles Treaty been more strictly enforced, World War Two would not have come about. And had the conditions of the treaty been arrived upon more quickly, when Germans had no choice but to admit that they'd been fully defeated on the battlefield and the revolution only saved Germany from the Allies entering German soil in action, as they did in 1945, the excuse that the treaty became would not have occurred. And the treaty did become a German excuse, and the "stabbed in the back" myth would arise, but more than anything it was the smashing of the Old Order that brought about the second war.
But was the collapse of the imperial order in nations that had not moved sufficiently towards democratic rule as populations moved from rural peasantry towards industrial laborers that really created the mess that would result in World War Two.
Almost every European nation had faced this in some fashion, but some had handled it much better. Nations like Germany, Austro Hungaria, and Russia, however, had not. Indeed, they'd not only failed to accommodate the new world of a more educated working class, but in Germany's case they'd actually arrived upon an autocratic imperial state late. Nations like France and Germany, in contrast, had moved more and more towards real democratic rule much earlier, and therefore the forces that would gather in the vacuum of the demise of the Old Order would not impact them in the same degree, or indeed in the democratic UK, at all.

In nations like Germany, Russia and (for WWI Allied) Japan, however, the demise of the Old Order would create a vacuum that would be filled by a vicious extreme forces, communistic or fascistic in nature, that opposed democratic rule and glorified martial violence. In some places those forces would oppose any hint at restoring the Old Order, as in Russia, in others they'd co-opt elements of it, as in Italy. In all such places, the result was to bring about disaster in every form.
When that war came, much of what the world had become acclimated to in the First World War would play out in horrific fashion. And much of that can be blamed on Germany, which had often acted just as barbarously in the Great War as they were to act in World War Two.
Germany had in large measure brought that defeat in the Great War upon itself. While people like to look back for some reason and imagine the Germany military of World War One and World War Two as hyper competent, quite the opposite was often true. While the Spring 1918 offensive was absolutely brilliant, Germany's dithering with the collapse of Russia guaranteed that a million men it desperately need on the Western Front would not be available. If Germany was stabbed in the back, it's own autocratic class and military leadership did the stabbing, as Germany set about advancing in a country it had already defeated and had helped push into civil war. It acted as if it had won the war, when in fact it had not.
Officers of the newly crated Third Army which was formed in France too late to see combat, but which would go on to occupation duty in Germany.
Of course the arms of the Western Allies cannot be ignored in that role. The ability of the British to rebound in the face of the 1918 offensive was magnificent, even if the common British view that they seemingly won the war on their own is exaggerated. The long suffering French deserve huge credit for the defense of their own country and carrying the war through to the end, which included the contribution of Marshall Foch whose coordinating the efforts of the Allies was a monumentally difficult task.
Drafted inductees into the U.S. Army, Los Angeles California, November 11, 1918. The U.S. continued to draft right up until the end of the war. I don't know what happened to men brought in this late.
And the US deserves much more credit than it is typically given by non American historians even if its military leadership deserves much more criticism than American ones will give it. The surprising ability of the U.S. to create a 4,000,000 man Army in just over a year's time, and to deploy 2,000,000 of them to France (and Italy) was a stunning achievement. The individual fighting qualities of the American soldier were also hugely impressive, although much of that was due to the soldier being very green and, frankly, poorly lead.
Paris crowd, November 11, 1918.
The U.S. Army, in fact, was committed to action in a manner that was to prove wasteful of lives as the American leadership persisted in the belief that there were no lessons to be learned from the Allies. The American effort was only able to get away with this as the Army was thrown into action at a time when massive force was likely to prevail against the Germans, even if it proved to be hugely costly. Indeed, real questions should be raised as to why the American leadership continued to persist in this fashion when even the very early efforts demonstrated how bloody such actions would be, even if the American willingness to endure the bloodshed, much like the Union's willingness to endure it in the latter half of the Civil War, guaranteed that an Allied victory would occur.***
American Red Cross works gathering in London for a parade, November 11, 1918, in honor of the war's end.
And it did so bring it about, even if it did not do so single-handedly. That sacrifice should not be forgotten.
_________________________________________________________________________________
*Before anyone points it out, yes I know that a state of war continued on until the execution of the Versailles Treaty, or even later if you consider that the US had to declare the war to be over unilaterally after the U.S. refused to enter into the treaty. Indeed, I've already been "corrected" on that once.
Well, whatever, but the war ended on this day. Germany wasn't going back to fighting under any circumstances, and couldn't, after entering into the Armistice on this day.
**The morose British war poet view of the war is largely a post World War Two view of it that reflects more than anything the state of the British mind following World War Two, which left Britain with an empire that it obviously was going to leave and with an utterly wrecked economy.
***The U.S. Navy, on the other hand, was really effectively commanded in the Great War and contributed enormously to a reduction of the effectiveness of German submarines. It's role, however, is largely forgotten.
Postscript
This day is also marked as Polish independence day, although it would be just as easy to pick a date several weeks earlier and indeed would perhaps be more accurate as various Polish political bodies had declared independence from Russia and Germany by this time.
There are several sad deaths often noted about the day. Augustin Trebuchon was the last French soldier to die in the war. He was 40 years old and had joined the French Army in August, 1914. A shepherd by trade, he'd fought the entire war. He had occupied the role of messenger throughout the war and knew that an agreement had been signed even when his unit went into action that morning, committed to an attack even with the knowledge that peace was likely to be soon agreed upon. That battle went on until 6:00 p.m., a good seven hours after the armistice had been signed, when the unit received word that the fighting had ended. French officials originally recorded his death as November 10, as they were embarrassed to admit that they had been fighting when peace was imminent.
George Lawrence Price was the last Canadian soldier killed. The 25 year old private originally from Nova Scotia was killed in a small unit action by a German sniper when they were reconnoitering some Belgian houses and discovered German machinegunners. He'd come into the Canadian army as a conscript the prior year, having been conscripted from his then home in Saskatchewan.
Private George Edwin Ellison was the last British soldier killed. The British cavalryman, age 40, had served for a time as a per war soldier and had been recalled into his old unit, the 5th Royal Irish Lancers, in 1914.
Charles I, the Austro Hungarian Emperor, announced he would give up the Austrian crown. He would do the same in regards to Hungary two days later. He never actually abdicated in hopes he'd be recalled. He wasn't.
Counter campaigns against Dutch socialist occured in the Hague.
British, Canadian and American troops, numbering about 600, engaged with a Red Army force of 2,500 at Tulgas, where the Armistice had no effect. About 1/2 the force were Americans. The combined unit had been attacked but after two days launched an Assault, 20th Maine at Gettysburg style, and drove the much larger Red unit back. Red Army casualties nearly exceeded the number of men total in the Allied force.
1919
Armistice Day, 1919.
Today was the first Armistice Day, now converted into Veteran's Day, in U.S. history. It came, of course, one year after the Armistice that had brought about an end to the fighting on the Western front in November, 1918.
Plans had been made in advance to celebrate the day, which of course was celebrated around the country.
In Central Wyoming the day's events were muted by the arrival of snow.
Which makes the day in 2019 a nice bookend. Snow again.
In Washington, the Prince of Wales was visiting and marked the day, which was likewise being celebrated in English speaking countries around the world.
1921 Warren G. Harding dedicated the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier in Arlington National Cemetery.
On this day in 1921 the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier was dedicated in Arlington National Cemetery. I noted that on our companion blog, Today In Wyoming's History, quite some time ago, but the photo below, of Chief Plenty Coups, whom I discussed on November 8, is a new addition here.
Also noting the tragedy of the Great War, today was the first day in which the Royal British Legion sold poppies in remembrance of the war. This tradition still goes on in the United Kingdom and also in Canada. When I was a kid, it occurred here in the form of artificial "bloody poppies" that were sold by one of the two veterans organizations, although I forget which one I dimly recall it was the VFW, but I could be in error.
Harding gave a speech, as noted, at the event, which was transmitted nationwide by telephone wires by AT&T.
A photographer played with black and while film to capture this image at 10:30 that evening.
The war with Germany officially ended on this day, not coincidentally, as the US and Weimar Germany officially recognized the peace. Germany also was reaching out to the Soviet Union with the formation of Deruluft, a joint German Russian airline. It operated until 1937.
The New York Bible Society presented a bible to the conference meeting in Washington on arms limitation.
1924 George Carr Frison, Professor Emeritus of Anthropology at the University of Wyoming born in Worland Wyoming.
1926 Plans for U.S. Highway 30, replacing the Lincoln Highway but generally along the same route, finalized.
1930 Clarence Don Clark, Wyoming's U.S. Congressman from 1890 to 1893, and US Senator from Wyoming from 1895 to 1917, died.
1940 Willys introduces their variant of the Jeep for the Army's competition for a light 4x4 vehicle. The very unstable dangerous little 4x4 car would enter into civilian production post war as the CJ2, the first really light commercially offered 4x4 truck (and a highly dangerous one). 4x4s would feature prominently in a revolution in accessibility to the Wyoming back-country post World War Two.
1958 M38A1, the military version of the same Jeep that was known as the CJ5.
1940 Here's an unusual item, although not a Wyoming one, that shows us, in part, how much things
have changed even in regards to weather reports. We're so used to
relatively accurate ones now, we don't recall the days when the weather
was often a real surprise. We should note that this winter event did stretch out across the plains to Wyoming, even though it didn't have the devastating impact here that it did in Iowa.
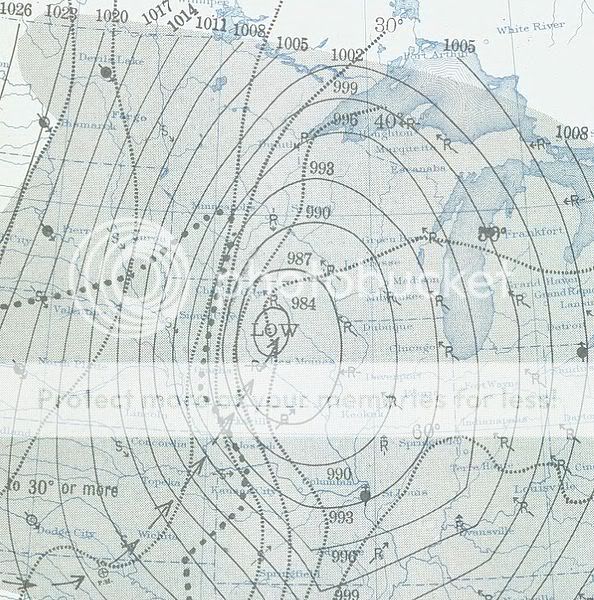
Iowa's 1940 Armistice Day blizzard.
1942 Congress lowered the age of conscription to 18 and raised the upper limit to age 37.
1943 The Commander of the Prisoner of War Camp in Douglas announced that 1,000 Italians held at the camp would be helping with the fall harvest. Given the timing of the announcement, it would have to be presumed that the harvest was well underway at the time. As Douglas itself is not in a farming belt, it would be interesting to know where the POWs actually went, and how they were housed. Attribution: Wyoming State Historical Society.
It was Armistice Day for 1943.
Japanese American Girl Scouts walking in front of barracks and carrying American flags while incarcerated at Heart Mountain concentration camp, Wyoming, 11/11/43.
1950 A DC-3 belonging to a religious missionary organization hit Mount Moran in dense cloud cover, killing all 21 people on board. The impact was nearly direct, and nothing from the plane could be recovered, including the bodies of the victims, all of whom remain on Mount Moran.